|
 |
Iron toxicity in
rice is still an under-researched topic |
 |
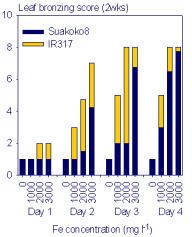
Iron (Fe)
toxicity is a major stress to rice in many lowland environments
worldwide. Due to excessive uptake of Fe2+ by the roots and its
acropetal translocation into the leaves, toxic oxygen radicals may
form and damage cell structural components, thus impairing
physiological processes. The typical visual symptom is the
“bronzing” of the rice leaves, leading to substantial yield losses,
particularly when toxicity occurs during early vegetative growth
stages. The problem is best addressed through genotype improvement,
i.e., tolerant cultivars. However, the time of occurrence and the
severity of symptoms and yield responses vary widely among soil
types, years, seasons, and genotypes. Cultivars resistant in one
system may fail when transferred to another. Better targeting of
varietal improvement requires selection tools improving our
understanding of the resistance mechanisms and strategies of rice in
the presence of excess iron. We have developed screening tools for
iron toxicity responses in rice genotypes. We have worked on a
method speeding up measurements of tissue Fe2+ concentrations and we
have been investigating effects of bacteria present in the
rhizosphere on the symptom responses of rice genotypes. |
 |
Iron toxicity |
|
PhD |
People |
 |
Katrin Engel
Genotypic Variability of Lowland Rice under Conditions of Iron
Toxicity, PhD Thesis 2014. |
|
MSc |
|
 |
"Mechanistische
Bewertung von Eisentoxizitätsresistenz bei Nassreis im Feldanbau im
Mekong Delta, Vietnam"
Diplomarbeit 2007, Sabine Stürz [Germany]. |
 |
"Physiological
mechanisms of iron toxicity in lowland rice"
Master of Science Thesis 2006, Tam Aung [Myanmar].
|
 |
"Developing
a Standardized Procedure to Screen Lowland Rice (Oryza sativa )
Seedlings for Tolerance to Iron Toxicity"
Master of Science Thesis 2003, Dilys Kpongor [Ghana]. |
|
Funds |
Projects |
|
 |
Phenotyping of lowland
rice for iron toxicity resistance - AfricaRice 2009-2010 |
|
 |
Evaluation of adaptation mechanisms of paddy rice to iron toxic
conditions - DFG 2008-2010 |
|
Paper |
Publications |
 |
Hartmann, J., Asch, F.
2018.
Micro-method to determine iron concentrations in plant tissues using
2,2' bipyridine. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, DOI: 10.1002/jpln.201700433.
|
 |
Engel, K., Asch,
F., Becker, M., 2012.
Classification of rice genotypes based on
their mechanisms of adaptation to iron toxicity. Journal of Plant Nutrition
and Soil Science 175, 871-881 |
 |
Engel, K., Asch,
F., Becker, M. 2012.
In-vivo staining of reduced iron by 2,2
bipyridine in rice exposed to iron toxicity. Journal of Plant Nutrition
and Soil Science, in press
|
 |
Becker,
M., Asch, F., 2005
Iron toxicity in rice -
conditions and management concepts. J. Plant Nutri. Soil Sci. 168,
558-573. |
 |
Asch,
F., Becker, M., Kpongor, D. S., 2005
A quick
and efficient screen for resistance to iron toxicity in lowland rice. J.
Plant Nutri. Soil Sci. 168, 764-773. |
|
Poster |
|
|
|
|
 |
Engel, K.,
Becker, M., Asch, F. 2009. "Efficiency
of Adaptation Mechanisms of Rice to Diverse Conditions of Iron
Toxicity". Tropentag 2009, October 6-8, University of Hamburg,
Germany. |
 |
Engel, K., Becker, M., Asch, F. 2008
"Adaptation mechanisms in rice cultivars of different
origin to iron toxic conditions". Tropentag
2008, October 7-9, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart
|
|
 |
Stürz,
S., Asch, F., Becker, M. 2007.
"Field validation of a quick screening method for iron toxicity
in lowland rice". Tropentag
2007, October 9-11, University of Kassel-Witzenhausen,
Witzenhausen.
|
|
 |
Asch, F.,
Aung, T., Becker, M. 2007.
"Root iron plaque formation as resistance mechanism to
iron toxicity in lowland rice". Tropentag
2007, October 9-11,University of Kassel-Witzenhausen,
Witzenhausen.
|
|
 |
Ripken,
C., Asch, F., Becker, M., Wimmer, M. 2005.
"A low cost miniature method to determine iron content
in samples suitable for small research laboratories".
Deutscher Tropentag 2005, October 11-13, University of Hohenheim,
Stuttgart.
|
|
|
 |
Iron
toxicity and root associated bacteria |
|
PD |
People |
 |
Dr. Le Thi
Thu Huong [Vietnam]
5 month visiting scientist grant from the "Food Security Center"
University of Hohenheim in 2013 and 2014. |
|
PhD |
|
 |
Tanja
Weinand
[Germany]
Bacterial mitigation
of iron toxicity symptoms in rice |
|
MSc |
|
 |
"Effects of rhizobacteria on root iron
plaque formation in rice subjected to iron toxicity"
Master of Science Thesis, Sunilda Terré [Spain] |
|
BSc |
|
  |
Einfluss
von Eisentoxizität auf
die Oxidationskraft von Nassreiswurzeln im Sortenvergleich.
Bachelor of
Science Thesis, Jadzia Hack [Germany] |

 |
Einfluss
endophytischer Bazillusstämme auf die Morphologie und
Oxidationskraft von Nassreiswurzeln
Bachelor of Science Thesis, Gideon Handschuh,
[Germany] |
 |
Basiert die Stressvermittlung durch Bazillus bei Reis auf der ACC-deaminase
Aktivität der beteiligten Bakterien?.
Bachelor of Science Thesis, Philipp Merx, [Germany] |
|

 |
Aufnahme und
Verteilung von endophytischen Bakterien in Reis.
Bachelor of Science Thesis, Sina Hartl
[Germany] |
|
Paper |
Publications |
 |
Dimpka, C.,
Weinand, T., Asch, F., 2009
Plant–rhizobacteria interactions alleviate abiotic stress
conditions. Plant, Cell, and Environment 32, 1682-1694. |
|
Poster |
|
 |
Weinand,
T., Asch, J., Asch, F. 2022. "Effect
of Bacillus spp. on enzyme activity and potassium uptake
in lowland rice (Oryza sativa) under iron toxicity.". Tropentag
conference 2022, September 14-16,
Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Czech Republic. |
|
 |
Weinand,
T., Schierling, T., Asch, J., Kaufmann, B., El-Hasan, A.,
Voegele, R. T., Asch, F. 2021. "Bacillus-mediated
cross-protection against iron toxicity and brown spot desease (Bipolaris
oryzae) in lowland rice.". Tropentag
conference 2021, September 15-17,
University of Hohenheim, Germany. |
|
|
|
Weinand,
T., Zeeshan, I.G., Hartmann, J., Asch, F. 2020. "Bacillus-mediated
changes in iron partitioning and sequestration in lowland rice
under iron toxic conditions". Tropentag
conference 2020, September 9-11,
Virtual Conference, Germany. |
|
 |
Terre, S.,
Asch, F., Becker, M. 2009.
"Influence of Bacillus spp. on iron plaque
formation at the root surface of lowland rice". Tropentag
2009, October 6-8, University of Hamburg, Hamburg.
|
|
 |
Terre, S.,
Asch, F., Padgham, J., Becker, M. 2007.
"Influence of root zone bacteria on root iron
sequestration in rice subjected to iron toxicity". Tropentag
2007, October 9-11, University of Kassel-Witzenhausen,
Witzenhausen.
|
|
 |
Asch,
F., Padgham, J. 2005.
"Root associated bacteria suppress symptoms of iron
toxicity in lowland rice"
Deutscher Tropentag 2005, October 11-13, University of Hohenheim,
Stuttgart.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|